- English
- Español
- Português
- русский
- Français
- 日本語
- Deutsch
- tiếng Việt
- Italiano
- Nederlands
- ภาษาไทย
- Polski
- 한국어
- Svenska
- magyar
- Malay
- বাংলা ভাষার
- Dansk
- Suomi
- हिन्दी
- Pilipino
- Türkçe
- Gaeilge
- العربية
- Indonesia
- Norsk
- تمل
- český
- ελληνικά
- український
- Javanese
- فارسی
- தமிழ்
- తెలుగు
- नेपाली
- Burmese
- български
- ລາວ
- Latine
- Қазақша
- Euskal
- Azərbaycan
- Slovenský jazyk
- Македонски
- Lietuvos
- Eesti Keel
- Română
- Slovenski
- मराठी
- Srpski језик
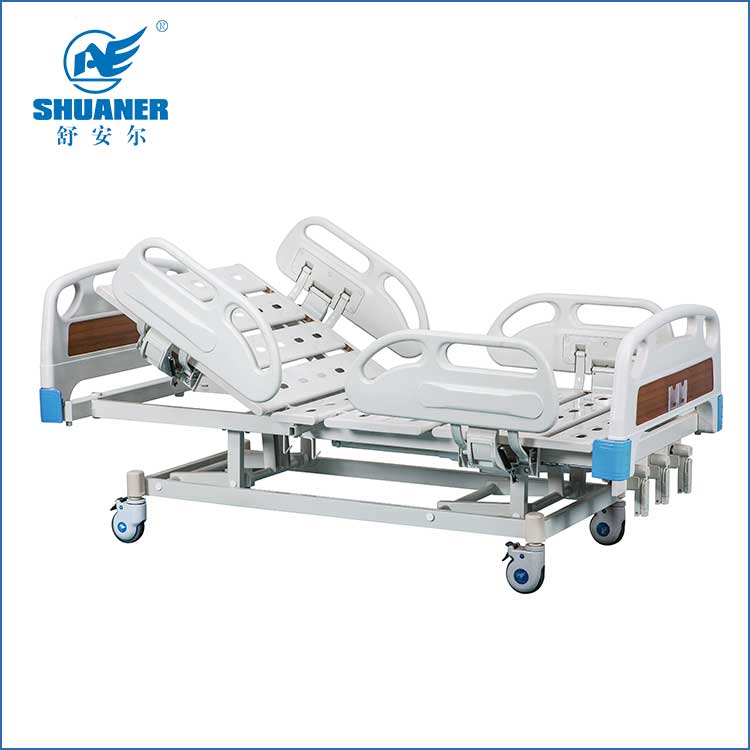
Precautions for using manual hospital beds
2024-12-26
Manual hospital beds are widely used in hospitals, nursing institutions and home care, especially for patients who need to stay in bed for a long time. When using manual hospital beds, in order to ensure the safety and comfort of patients and extend the service life of the bed, the following aspects should be noted:
1. Preparation before adjusting the bed
Check the stability of the bed: Before making any adjustments, make sure that the bed is firmly placed on a flat ground to prevent tilting or sliding during adjustment.
Ensure the cleanliness of the bed: Check whether the bed surface and mattress are clean to avoid foreign objects affecting the function of the bed or the comfort of the patient.
Patient posture: Ensure that the patient's posture is appropriate to avoid discomfort or physical injury during bed adjustment. It is best to keep the patient lying flat during the adjustment process.
2. Precautions when adjusting the bed
Avoid excessive adjustment: When adjusting the angle of the bed (such as backboard, leg board, etc.), avoid excessive adjustment, especially for patients with severe conditions or fractures, excessive angles may cause discomfort or further injury.
Gradual adjustment: Each adjustment should be made step by step to avoid rapid and violent movements to ensure that the patient can adapt to the change of bed position.
Check the bed status: During the adjustment process, make sure that all adjustment devices (such as handles, pull rings, etc.) are intact to avoid loosening, falling off, etc. during the adjustment process.
3. When adjusting the angle of the bed surface
Back tilt angle: When adjusting the backboard, it is recommended to start from a small angle and gradually increase it to avoid adjusting too much at one time, especially for patients with spinal problems.
Leg angle adjustment: When adjusting the leg support, make sure that the patient's knees are not compressed to avoid blood circulation problems. For patients with lower limb problems, be especially careful to avoid discomfort caused by legs being too high.
Reverse adjustment: If the bed surface is designed with a reverse adjustment function (such as the "zero gravity" mode), it can be adjusted according to the patient's needs. This mode can help relieve the pressure on the patient's back and waist and improve comfort.
4. Patient comfort and safety
Mattress selection: To ensure the patient's comfort, the bed should be equipped with an appropriate mattress. The mattress should meet the patient's body shape and condition requirements, and avoid mattresses that are too hard or too soft to affect sleep quality or cause bedsores.
Preventing bedsores: For patients who are bedridden for a long time, adjust the patient's lying position regularly to avoid bedsores caused by long-term pressure concentrated on a certain part.
Bedside guardrails: If the patient's mobility is weak, it is necessary to use bedside guardrails to prevent the patient from falling off the bed. Make sure the guardrails are firm and undamaged.
5. Cleaning and maintenance
Regular cleaning: Manual beds should be cleaned regularly, especially the bed surface, bed board and bed frame of the bed to prevent stains from accumulating and affecting the function of the bed.
Check the bed frame and adjustment device: Regularly check whether the various adjustment devices of the manual bed (such as lifting handles, bed surface adjustment devices, etc.) are normal to ensure that each component operates smoothly and prevent wear or looseness from affecting use.
Lubricate manual parts: Regularly add lubricating oil to the manual adjustment device (such as the bed board adjustment lever, etc.) to maintain its flexibility and avoid operating difficulties or damage due to excessive friction.
6. Pay attention to safety during use
Prevent accidental sliding: Make sure the casters of the bed are locked to prevent the bed from accidentally sliding during adjustment.
Prevent patients from adjusting the bed by themselves: Some patients may try to adjust the bed by themselves, especially those with a certain degree of mobility. Patients should be prevented from operating the bed without authorization to avoid injuries caused by improper adjustments.
Avoid overloading: Do not place items on the bed that exceed its load-bearing range. Usually, beds have clear load-bearing limits, and overloading may affect the stability and durability of the bed.
7. Pay special attention to special conditions
Patients with fractures: For patients with fractures or osteoporosis, be particularly careful when adjusting the bed to avoid large or sharp movements.
Patients with respiratory diseases: For patients with respiratory problems, such as respiratory failure, pneumonia, etc., raising the head appropriately can help breathe smoothly, but avoid excessive head angles.
Patients with heart disease: For patients with heart disease, avoid sudden changes in the bed angle, especially adjustments of the head and legs, to prevent blood pressure fluctuations or increased heart burden.
Summary,The correct use of manual hospital beds can effectively improve the comfort and safety of patients, and also help the work efficiency of nursing staff. During daily use, special attention should be paid to the stability of bed adjustment, patient comfort and bed maintenance. Through correct operation methods, potential safety risks can be reduced and the health of patients can be guaranteed.